- Conserving energy means protecting, preserving and managing energy resources well.
- We have already learned about the types of energy and their sources.
- If the sources of energy are destroyed, or if we do not use the energy wisely, we may not have enough energy for use in the future. We, therefore, need to conserve energy.
- Some of the methods of conserving energy include:

Most people in Kenya use jikos and cooking stones when cooking.
Jikos burn charcoal or firewood as a source of energy.
Charcoal is made from wood, which is a renewable source of energy.
If more trees are felled to produce charcoal and few trees are grown, we will run out of trees which are an important source of energy in our country.
The use of energy-efficient devices will help reduce the amount of wood fuel consumed in a particular period of time.
An improved jiko is an example of an energy-efficient device.

Using energy sparingly means using it carefully to avoid unnecessary loss.
Energy is very important to us, and we have to use it sparingly so that we have enough in the future.
We can use energy sparingly by doing the following:


Comparison between traditional and improved jiko.


Sources of energy that cannot be exhausted are called renewable sources of energy.
Those that can be exhausted are termed non-renewable sources.
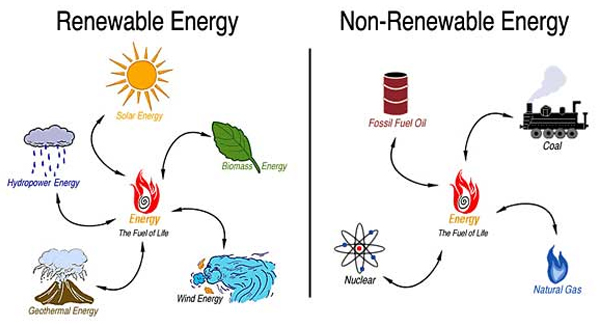
Examples of renewable sources of energy include:
Wind refers to moving air.
Wind has energy.
The energy from wind can be used to turn turbines in windmills, which convert the wind energy into electricity.

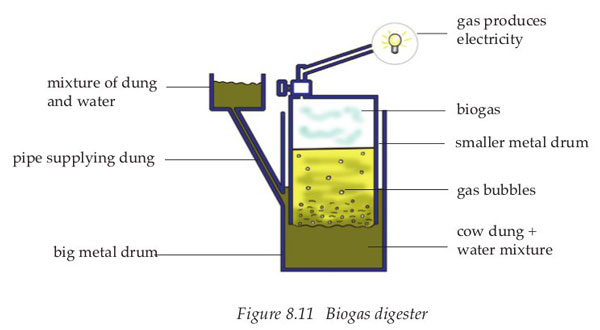
To make biogas you need a digester.
Place two amounts of water to one of cow dung in the digester.
As the dung ferments, biogas is produced.
The biogas rises to the top of the small metal drum.
A control tap directs the gas to either cooking or lighting area.
The remaining dung can be removed and used as manure.
Below is a biogas digester.
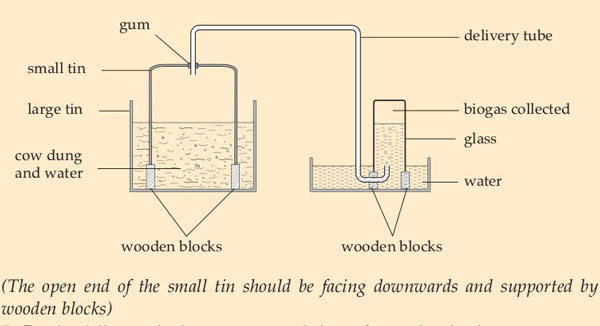
Below is a diagram on the production process of biogas
The sun is the main source of energy.
Energy from the sun is also known as solar energy.
Solar energy is used in the following ways:
Manufactured food in plants is transferred to animals when they eat plants.
Solar panels can be used to trap solar energy.
The energy can then be used to heat water or to light houses.
Heat energy from the sun can also be used to dry harvested crops.

Trees are important to the environment because they :
The government of Kenya advises us that every time we cut down one tree, we should plant two.
This is aimed at restoring the forest cover. At the moment, however, the rate of cutting down trees is higher than the rate of planting and growing them.
This is why our forest cover is declining. Scientists believe that forests should cover at least 10% of the total area of a country.
Our forest cover, however, is only 1.7%, and this may be the reason why our rivers and lakes are drying up.
Afforestation is the planting of new trees to create forests. Reforestation is the planting of trees to replace those that have been cut.
To grow trees in a school compound
What to do
1. The diagram below shows an apparatus that can be used to produce biogas from decaying cow dung. The apparatus has four taps labeled M, N, O, and P.
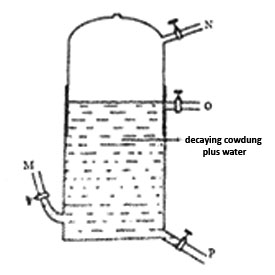
Which tap is the outlet for the gas?
A. M B. N C. O D. P
2. The diagram below represents an improved jiko that conserves energy.
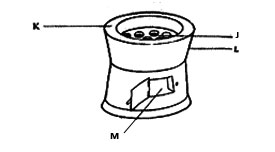
Which one of the following explains how the jiko conserves energy?
A. L is a good conductor of heat.
B. M lets in a lot of air into the jiko.
C. Space J holds only a small amount of charcoal.
D. K is a poor conductor of heat.
3. The diagram below represents a solar heater.
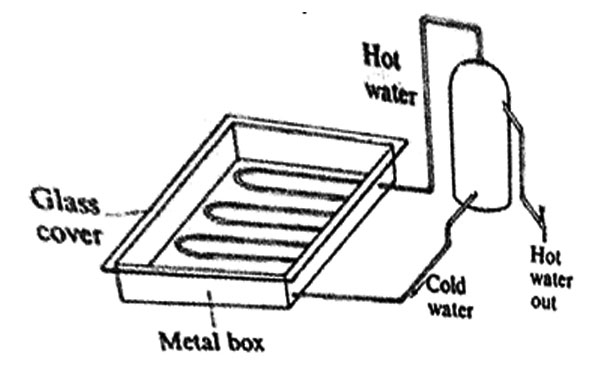
Which of the following would make the water heat up faster?
A. Painting the pipe black and the inside of the metal box white.
B. Painting the glass cover white and the inside of the metal box black.
C. Painting the pipe black and reducing the number of coils.
D. Painting both the pipe and the inside of the metal box black.
4. Gatiku was provided with a metal jiko. Which one of the following would she do to improve the jiko so that it conserves energy?
A. Add a second layer of metal on the outside of the jiko.
B. Close the air opening at the side of the jiko.
C. Smear the outside of the jiko with ash.
D. Plaster the inside of the jiko with mud.
5. The MAIN reason why people should be encouraged to use the improved jiko is that it
A. It is more expensive to use charcoal than firewood.
B. It helps to conserve forest resources.
C. It is easily made from locally available materials.
D. It does not produce much smoke.
6. Which one of the following statements about the use of cow dung in the biogas digester is NOT TRUE?
A. Heat is produced B. Bacteria decompose the dung
C. Mineral salts are destroyed D. Gas is produced