Light helps us to see things.
Without light we would be in darkness.
When you are able to push or pull an object through a distance in the direction of the push or pull then you have done some work.
Energy is what one uses to do work.
Energy is what a bulb, for example, uses to light up, or what a magnet uses to attract a nail.
We need energy to do a lot of things for example for lighting, cooking, ironing, and listening to the radio.
 [resource: 1423, align: left][resource: 1424, align: left]
[resource: 1423, align: left][resource: 1424, align: left]
The types of energy are:
Light comes from things that are living things while others are non-living things.
Examples of living things that give out light are fireflies and glow worms.

Examples of non-living things that give out light are the sun, a burning candle, fire, a torch, burning lamp, and electricity.

These things that give out light are called Sources of light:
Anything that produces its own light is referred to as a source of light.
One characteristic of light is that it travels in straight lines.
This means that light cannot go around bends.
When light meets an object on its way, the following may happen :
When an object stops all the light some darkness forms behind the object.
This dark patch is known as a shadow.
The shadow normally takes the shape of the object blocking the path of light.
The size of the shadow varies depending on the distance between the source of light and the object.
The house needs to be well lit during the day and at night.
We can light our houses in the following ways:
This type of roof allows sunlight to get into the house during the day.
Examples of artificial lighting are:



Light is made up seven different types of lights.
Therefore each ray of light has these seven colours of light. Each of the seven lights has a different colour. The colours are Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet.
You can pronounce the first letters of these lights as ‘ROYGBIV’ in order to remember them.

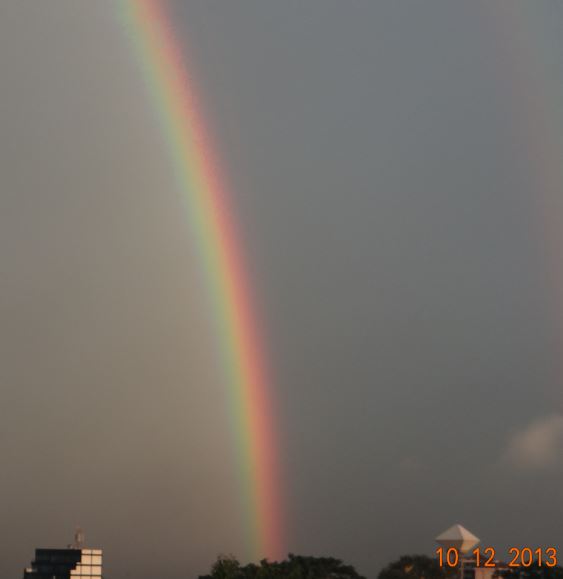
These colours form the rainbow. A rainbow is normally formed when light is split into each of these colours.
The inner colour of the rainbow (the smallest curve) is violet while the outer colour (largest curve) is red. Therefore the colours in the rainbow appear in the order shown in ‘ROYGBIV’.
A rainbow is formed when light travels from one media through another media and out again into the first media.


As the light passes from the air into water it is refracted. It meets the mirror in the water and is then reflected back by the mirror from the water into the air where it is bent further.
Therefore the bending of light as it passes from one media into another (refraction) and back again to the original.
Light travels in all directions through a ray.
A ray is the straight line along which light travels. We see objects because light leaves the object through many rays and travels to our eyes.
To show that light travels in a straight line :
1. Stand three identical cardboards having a hole at the middle in a dark room as shown.
2. Pass a string through the holes to make sure the holes are in a straight line.
3. Shine a source of light for example a candle at one end of the three cardboards
4. Look through the other end of the cardboards.
You can see the light from the other end of the cardboards. Now displace one of the cardboards so that its hole is not in line with the other two holes.
You will not see the light through the holes but instead you will see the cardboard. This is because the light from the source could not go round the cardboard into the displaced hole to reach your eye.
Therefore, light travels in a straight line.
Any material that allows light to pass through it is called a transparent material. Examples of transparent materials are clear glasses, clear water and air.
Transparent materials allow all light to pass through them. This means that you can see light or any object that is behind a transparent object.
Any material that allows only some amount of light to go through it is called a transluscent material.
Not all light passes through translucent material. This means that you cannot see the light as clearly as you would see it through a transparent material.
Examples of translucent materials are waxed paper (tracing paper) and frosted glass (the glass used in bathroom and toilet windows).

Any material that does not allow any light to pass through it is called an opaque material.
This means that you cannot see any light through an opaque object.
Examples of opaque materials are a block of wood, stones, and a book.
When light meets an object on its way it may either be stopped and absorbed by an object or it may bounce off the object like water depending on the type of the object.
When light bounces off an object we say the light has been REFLECTED by the object.
For an object to be able to reflect light it has to be shiny. Any shiny surface reflects light.
Mirrors are the best examples of shiny surfaces.
When you hold an object in front of a mirror, you are able to see the image of the object from the mirror.
This happens because the light from the object is shone to the mirror from where it bounces to your eyes.
Light travels in a straight line through one transparent material or media such as air, glass, and clear liquids.
However, this behaviour changes when light travels from one medium to another, for example from air to water.
Light changes direction at the point where light gets from one medium to the other. It changes its path and bends.
This change of direction and bending of light as it moves from one medium to the other is known as refraction.

When you place a ruler into a glass of water at an angle and view the ruler from the side of the glass the ruler APPEARS bent.
The tendency of the ruler to appear as if it is bent, can be explained as follows:

Before light reaches your eye, it passes from the water into the air then it gets to your eyes.
By passing through the two media (air and water), you see as if the ruler is bent. Yet this is not true.
We say it is apparent.
If the ruler is removed from the water it will appear straight as before.
Similarly a pencil or a stick when partially submerged in water will appear bent.
Therefore, refraction is the apparent bending of light when it travels from one medium to another.
Standard 6
1. Which one of the following shows the correct order of the four colours as they appear in a rainbow?
A. Indigo, blue, green, violet B. Blue, green, violet, indigo
C. Green, violet, indigo, blue D. Violet, indigo, blue, green.
2. As Katinda was walking from home to school early in the morning, she saw her shadow on her right-hand side and the school directly ahead of her. In which direction was the school from where she was?
A. East B. West C. North D. South
1. A Standard VII teacher arranged an apparatus to show that heat from the sun can be used for cooking. The apparatus was arranged as shown in the diagram below.
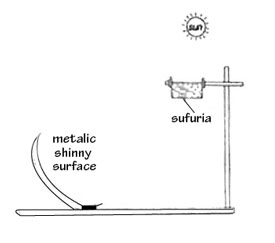
Rays from the sun were transferred to the sufuria from the curved shiny surface by
A. Dispersion B. Reflection C. Absorption D. Refraction
2. A periscope is used for
A. Observing the sky at night B. Observing objects around corners
C. Making objects appear closer D. Making objects look bigger
3. Chebet drew an object and placed a mirror in front of it as shown in the diagram below.
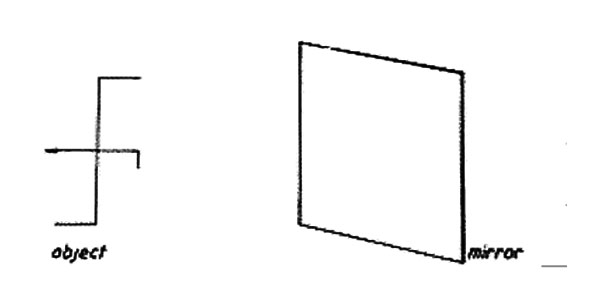
Which one of the following correctly shows the appearance of the image as seen in the mirror?
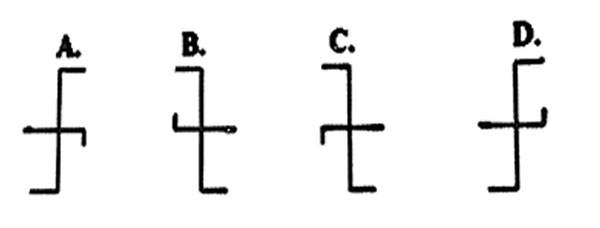
4. A fisherman looks down into a lake and sees a stationary fish as shown in the diagram below.
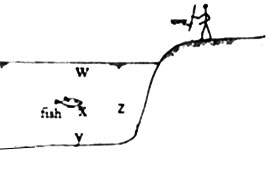
At what point should he aim his spear in order to have the BEST chance of hitting the fish?
A. W B. X C. Y D. Z
5. Kamau filled a transparent bottle with water and then covered it completely with black paper and made a small hole, v, on one side and four other small holes, w, x, y and z on the opposite side. He shone light from a torch into the water as shown in the diagram below.
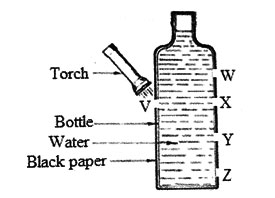
At which point is the light most likely to shine out?
A. W B. X C. Y D. Z
6. The diagram below represents a periscope, an object and an observer’s eye
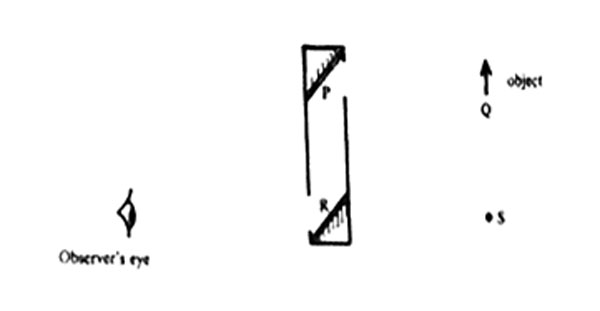
The image of the object as seen by the observer will appear at
A. P B. Q C. R D. S
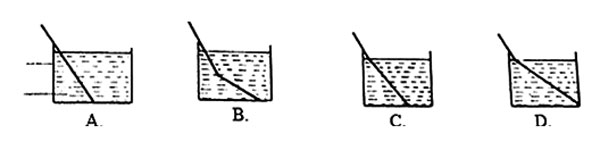
7. Kijita dipped a ruler in water in a glass container.
Which of the following diagrams shows how the ruler appeared when
viewed from the top of the glass?
8. A periscope is an instrument used to observe
A. The sky at night B. Objects round corners
C. Objects far away C. Very tiny objects
9. A man wearing a T-shirt labeled LION stood in front of a plane mirror. Which one of the following shows the CORRECT image of the word LION?
