
A language group is a group of people who speak similar or related languages. This means that when they speak, they are able to understand one another to some extent.
Africa has many different groups of people living in it. We shall cover this section by dividing the continent into the following regions;
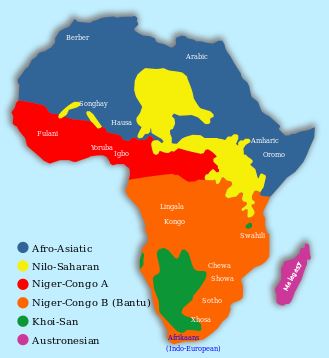
Some of the Major Language Groups of Africa
| People | Country |
| Swazi | Swaziland |
| Xhosa | Republic of South Africa |
| Zulu | Republic of South Africa |
| Sotho | Lesotho |
| Herero | Namibia |
| Tswana | Botswana |
| People | Country | |
| Shona | Ndebele | Zimbabwe |
| Bamileke | Cameroon | |
| Yao | Makua | Mozambique |
| Bemba | Lozi | Zambia |
| Nyanja | Chewa | Malawi |
| Bakongo | Balunda | Democratic Republic of Congo |
| Mbundu | Angola |
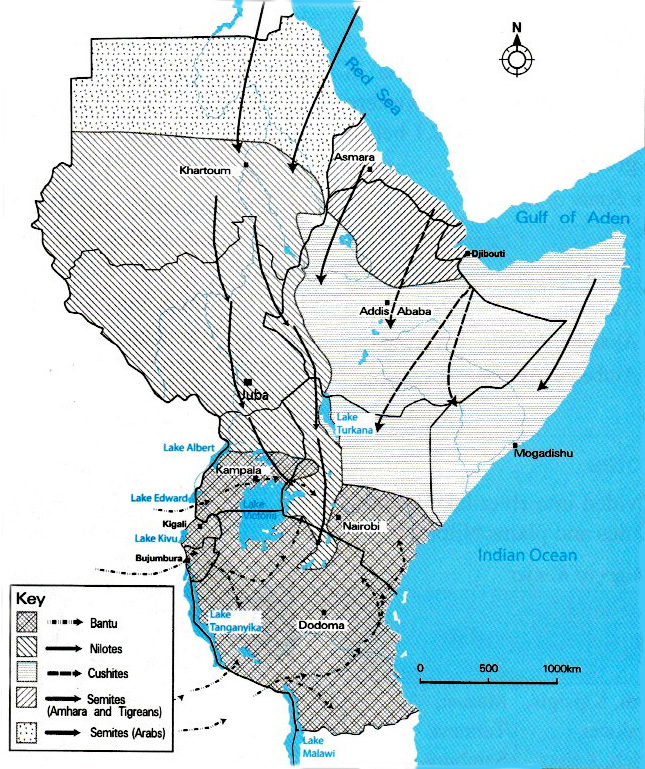
Bantus are believed to have originated from the basin of River Congo, Cameroon and parts of West Africa. Their main economic activities include crop cultivation, livestock farming and trade.
| Kenya | Uganda | Tanzania |
|
|
|
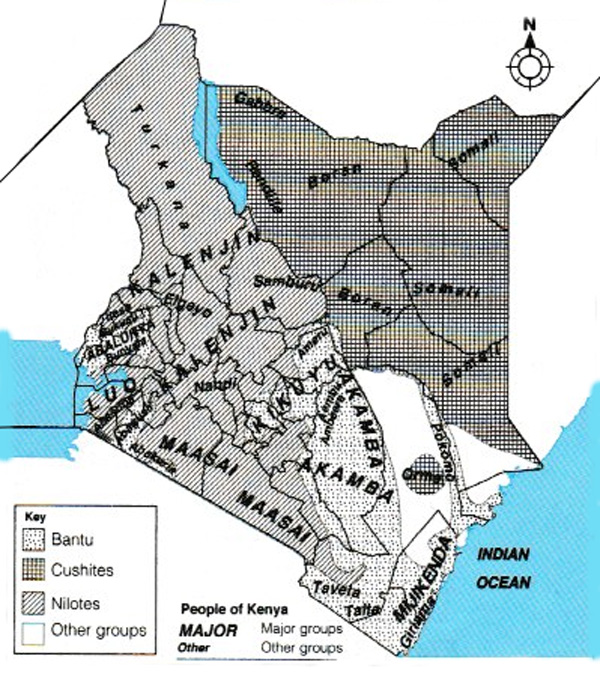
Nilotes are believed to have originated from the Nile Valley. Nilotes are mainly found in the Southern half of Sudan, Northern Uganda, the lake regions of Kenya and Tanzania.
Nilotes are divided into three sub-groups;
They are mainly found in Kenya, Uganda and Sudan. Their main economic activities include livestock farming and fishing.
| Kenya | Uganda | Sudan | Tanzania |
| Luo |
Acholi Alur Langi Labwor |
Dinka Nuer Shiluk Anuak |
Luo |
They are mainly found in Kenya. Their main economic activities include crop cultivation and livestock farming.
| Kenya | Uganda | Tanzania |
|
Nandi Kipsigis Pokot Keiyo Tugen Sabaot Marakwet |
Sebie Suk |
Dadog |
They are mainly found in Kenya and Tanzania. Their main economic activities include livestock farming.
| Kenya | Uganda | Sudan | Tanzania |
|
Maasai Iteso Njemps Samburu Turkana |
Iteso Jie Karamjong |
Jive Kuku Donviro |
Maasai |
They are mainly found in Somalia, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea and Djibouti. They are believed to have migrated into Eastern Ethiopia across the Red Sea from the Arabian Peninsula before 2 000 BC. Their main economic activity is livestock farming.
| Kenya | Tanzania | Ethiopia |
|
Somali Rendile Orma Galla Gabbra Boran |
Hawa Burungi Iraqw Sandawe |
Bilin Bedawiye Afar Salas Boran Sindano |
Semites have Jewish, Arabic and African blood.
Their main economic activity was trade.
They include;
Other communities found in Africa are;
Asians: These people first came to Africa from India and Pakistan as traders along the coast.
More Asians came into the country during the construction of the Kenya-Uganda Railway.
Today, many Asians live in urban areas where they work as traders and business people.
Europeans: Europeans first came to Africa as explorers, traders and missionaries. Later, some Europeans came into the country as farmers and colonial administrators. Most of them came from Britain, France, Germany, Denmark and Italy.
Some Europeans came into Africa just for adventure but they settled there.
Some of them are citizens of different African countries.
In the past, communities in Africa migrated from one place to another because of the following reasons: