We must control parasites or pests bothering them, through medical care or preventing and controlling the parasites.
Parasites are living things that depend on other living things for food.
They live within or on the body of the organism they depend on, or inside the body of the organism.
The organism which the parasite depends on is referred to as the HOST.
There are two types of parasites: ExternalPARASITES and Internal PARASITES
External parasites are found outside the body of the animal attached to the skin of the animal.
These parasites feed on the blood of their host by sucking their blood.
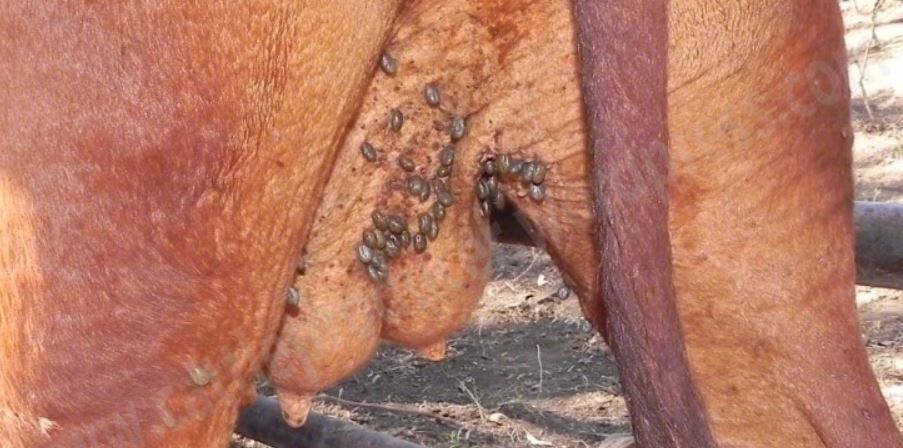
Examples of external parasites are ticks, fleas, mites and tsetse fly.
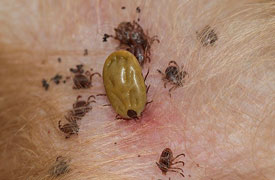 tick
tick
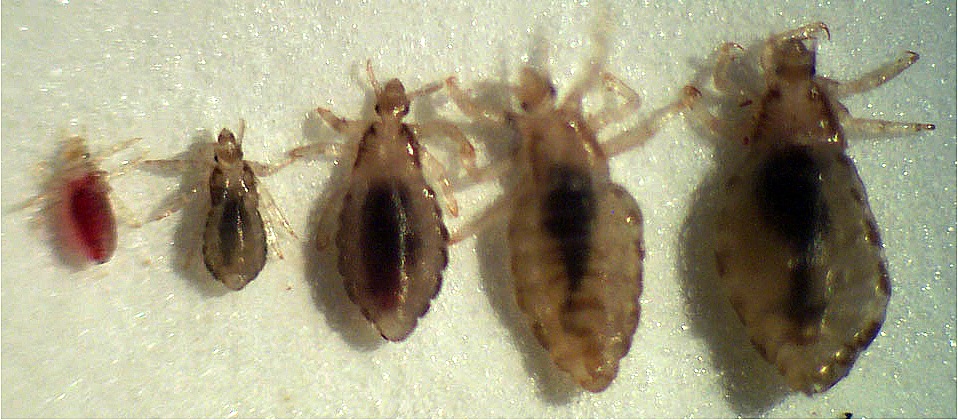 lice
lice
• They suck blood from the animal and make them suffer from anaemia.
• They transmit diseases to the animals.
• They damage the skin or hide making them to have low value and so the farmers lose on profit.
• They cause irritation on the animal and make them irritable and uncomfortable.
• The animals may eventually die from the diseases transmitted.
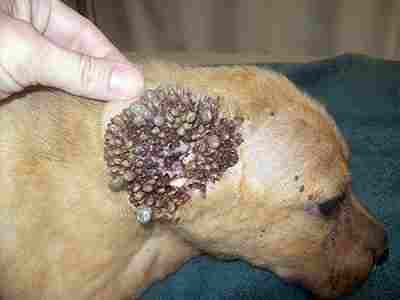 Ticks on a Dog
Ticks on a Dog
1. Dipping or spraying the animals with Acaricide
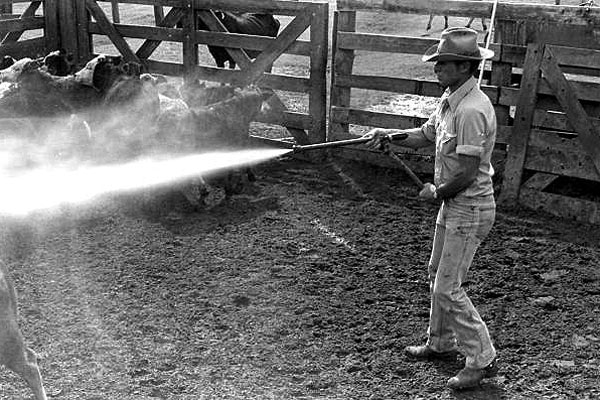

2. Hand picking the ticks from the animals and destroying them by burning.
3. Hard dressing the animals with some medicine on the skin.
4. Applying some powder medicine inside the animal house to kill the parasites.
5. Practising rotational grazing denies the parasite a host when the livestock is moved to a different area.
Internal parasites live inside the body of the host.
Examples of internal parasites are liver flukes, tapeworm, roundworms and hookworms.
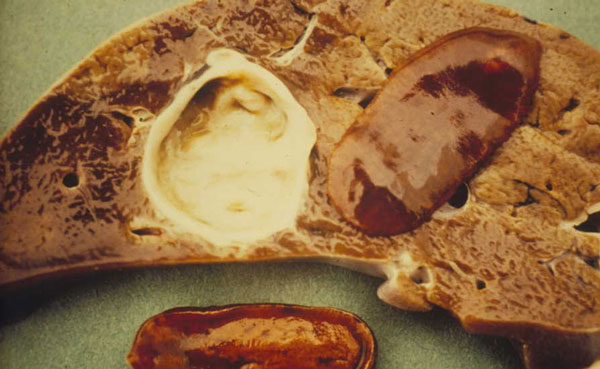 liver flukes
liver flukes
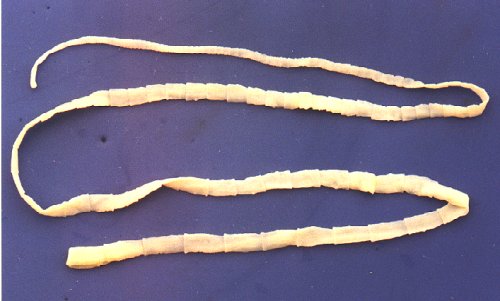 Tape worm
Tape worm
1. They can cause damage to the body organs such as the liver and the digestive system.
2. They can cause blockage to the body organs for example the intestine which may be fatal, like in the case of tapeworms.
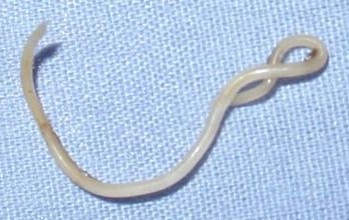 Roundworm
Roundworm
3. Produce poisonous products inside the animal’s body that make the animal sick
4. They eat the food meant for the animal making it weak.

5. They may suck the blood making the animal to have insufficient blood causing anemia.
1. Deworming livestock kills the parasites.
Deworming is done by giving livestock liquid drugs (drenching) tablets by mouth (dosing).
2. Killing water snails using drugs called molluscicidal.
3. Draining swampy areas to reduce snail habitats.
4. Rotational grazing denies internal parasites a host.
5. Burning pasture like grass kills the parasite's eggs deposited on them.
1. The animal may look thin and weak.
2. Some parasites like fleas, mites on chicken or ticks on cattle and sheep can be seen with the naked eye.
Some pests can be seen in the dung for example tapeworm.
3. The animals scratch themselves against walls, fence, and bushes.
4. The animals’ coats look rough and dull.

5. Some animals cough or sneeze and produce excessive mucus for example when sheep have maggots in the nostrils.
6. Animals may diarrhoea caused by internal parasites.
7. Animals may develop pot-belly appearance due to many internal parasites.
Standard 7
1. A teacher was teaching common pests of crops and animals to a standard VII class. He brought the following pests to class.
|
Fleas |
Weevils |
|
Flukes |
Lice |
|
Ticks |
Stalkborer |
Which one of the following sets is made up of animal pests only?
A. Ticks, lice, stalk borer, flukes
B. Weevils, stalk borer, lice, flukes
C. Ticks, lice, flukes, fleas
D. Weevils, fleas, lice, flukes
2. Which one of the following livestock parasites CANNOT be controlled by spraying a chemical on the animal?
A. Ticks B. Fleas C. Tsetse-flies D. Mites
3. Which one of the livestock parasites illustrated below is an internal parasite?
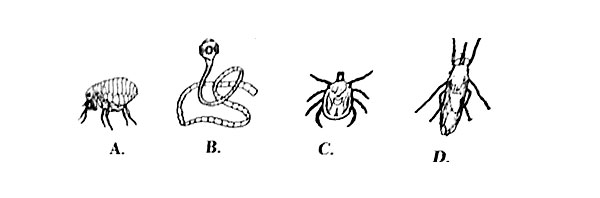
4. Which one of the following parasites CANNOT be controlled by rotational grazing.
A. Ticks B. Tapeworms C. Tsetse flies D. Liver flukes
5. A farmer would like to give medicine in solid form to cattle through the mouth to control internal parasites. Which one of the following equipment is the right one to use?
A. Bolus gun B. Syringe C. Drenching gun D. Bottle
6. Which one of the following parasites is controlled by both the drenching of animals and the draining of stagnant water in the farm?
A. Ticks B. Roundworms C. Tsetse flies D. Liver flukes