A forest is a group of trees growing together over a large area. Forestry is the practice of developing new forests or managing and maintaining the already existing forests.
Types of forests
There are two types of forests:
a) Natural forests
b) Planted or man-made forests
Distribution of natural forests in Africa
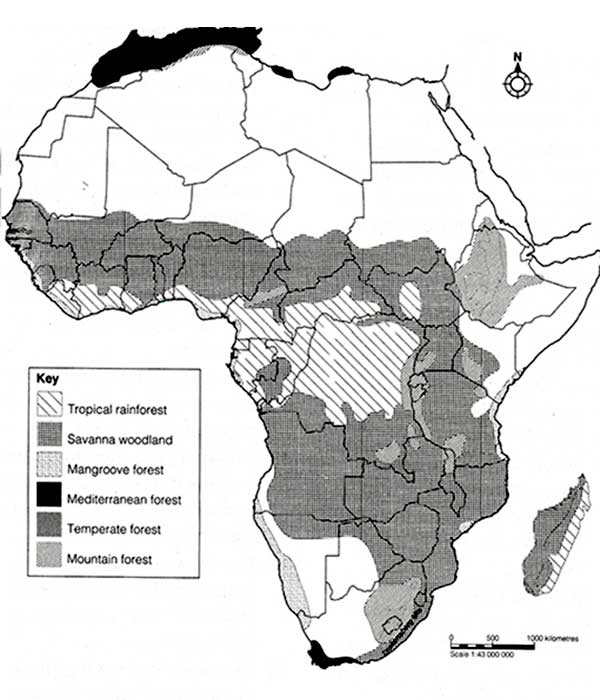
These can be divided into the following types:
i) Tropical forests
ii) Mangrove forests
iii) Temperate forests
These forests are generally found in hot equatorial lowlands which receive more than 1200 mm of rainfall. The tree species found here are mainly hardwood species. They always appear green all the year round. Therefore, they are known as evergreen forests. In Kenya, equatorial rain forests are found along the Kenyan Coast, around Kakamega and near the Lake Victoria Basin. It is however, important to note that a large portion of these forests have been cleared.
These are water loving plants that grow in salty water along the Coast of Africa. They mainly grow along the Eastern Coast of Africa; especially along the Coast of Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique and Madagascar. They have aerial roots which remain on the surface of the water to get air.

These forests are mainly found in highland areas where temperatures are low. In Africa, they are found on the slopes of highland areas like Mount Kilimanjaro and the Ethiopian Highlands. In Kenya, these forests are mainly found on the slopes of Nyandarua, the Mau Ranges, Cherang’anyi Hills, Mount Kenya and Mount Elgon. The tree species found in temperate forest include: the Meru oak, cedar and camphor.

These are forests that have been planted by people. They are usually of the same tree species and often appear in straight lines. A lot of Kenya’s forest cover has been cleared. The process of clearing forests is called deforestation. Most of these trees are soft wood. Examples of planted trees are: cypress, pine and eucalyptus. Today, only about 1% of Kenya’s land surface is covered by forests. This is dangerous as it is likely to affect the environment, for example increasing global warming.
Many natural forests in different parts of Africa have been cleared. This is mainly because of high population increase on the continent which has created need for more land. Kenya has very few forests, covering about 1% of the total area of the land.
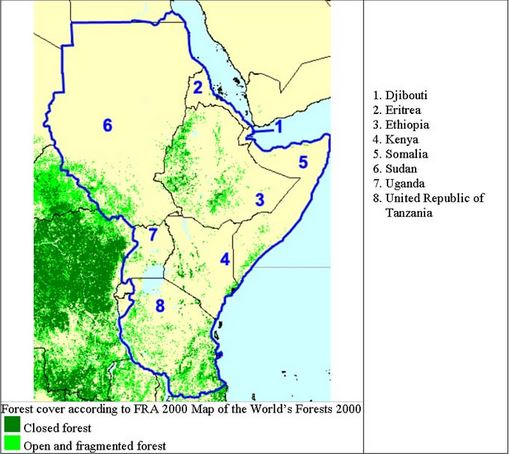
The image below shows natural forests in East Africa
These forests are found in DRC, Cameroon, Ghana, Cote d'Ivore, Togo, Guniea Bissua and east coast of Madagascar. The largest equatorial forest is the Congo forest.
They are found in most parts of Africa. They are made up of trees like acacia, baobao and are characterised by shurbs.
These forests are found along the coast of Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria. They are also found in South Africa.
They are found on the slopes of mountains and highlands found in Africa.
They grow on shallow marine water along the east coast in Africa and adjacent islands.They are found along the coast of Kenya, Tanzania, Western coast of Mozambiqie, Madagascar, Nigeria, Liberia and Gadon.
Forests act as water catchment areas. Therefore, many rivers have their sources in forests.
Hardwood timber and other timber products are exported to earn country foreign exchange.
Tree roots bind the soil particles together which help to reduce soil erosion.
As leaves fall on the ground, they rot and turn into humus increasing soil fertility.
Forests are home for wildlife. Wild animals attract tourists who bring foreign exchange in the country.
In rural homes, trees are an important source of wood fuel;they do provide firewood and charcoal.
Trees produce timber and posts which are used to build houses,making fencing posts, furniture and boats.
Wood obtained from trees is an important source of raw materials for pulp and paper industry.
1. Forest fires are common during the dry season. Some of them are caused accidentally by careless smokers while some are lit by people deliberately. Some fires are caused by lightening during thunderstorms.
2. Small insects called aphids attack softwood trees in planted forests making them to dry up.
3. Many forests are cleared through deforestation. This is because of settlements and farming.
4. Over exploitation of forests for timber, charcoal and firewood.
5. High demand for forest products leads to legal logging.
6. Some wild animals like elephants damage trees as they graze in the forests.
7. Forests are affected by drought and a decrease in the amount of rainfall.
8) Poor gorvenment policies on forest management and degazzment of forests reserves which allow people to settle in the forest
9) Over exploitation of forest for timber, charcoal and firewood.
10) High demand for forest product leads to illegal logging.
11) Some wild animals like elephants damage trees us they graze in the forest
12) Forest are affected by drought and a decrease in the amount of rainfall.
Forest conservation measures is the preservation and management of forests. Forest conserservation measures include:
1. Gazettement of forest reserves.
This protects the forests from human encroachment. Thus,people are not allowed to settle or cut trees in the forest in the forests.
2. Agro-forestry.
This is planting of trees together with crops on the same farm. Farmers are encouraged to do so as it will increase the forest cover.
3. Afforestation and re- afforestation.
The government encourages tree planting activities in the country where there were none,this is called afforestation. It also encourages people to plant trees to replace the ones cut,this is called re-afforestation.
4. Banning illegal logging.
The government has put measures involving the cutting of trees. To do so, one has to acquire license. This has reduced illegal logging.
5. Establishnebnt of tree nurseries.
These have been set up to provide people with tree seedlings to plant.
6. Fencing the forests.
Fences have been put up around forest reserves to prevent people from getting into the forest to cut trees
7. The government protects and conserves indigenous tree species.Some forests and shrines that have such trees have been protected and declared national heritage.
8. Forest fires need to be spotted early and put out before they spread and destroy large areas of forests.
9. Establishment of forest research and training centres to carry out research on better ways of managing and presrving forests.
10. Use of alternative sources of energy instead to firewood and charcoal, such as biogas, solar energy and electricity.
11. Carrying out campaigns to educate and create awareness on the importance of forests.
12. Involving the non-governmental organisations and the private sector in the management of forests and planting trees.
13. Encouraging the recycling of paper products from trees so as to minimise the exploitation of trees for paper making.
14. Use of energy saving jikos which use less charcoal or firewood to cook . This reduces the exploitation of trees for wood fuel.
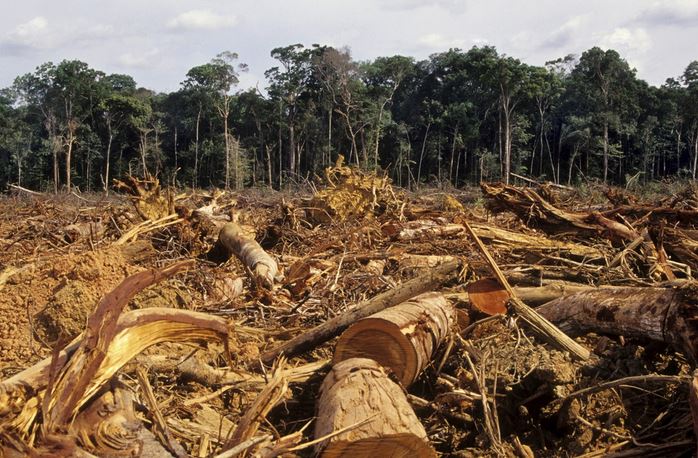
Here is an image of a forest which has been cut down.

Most forests in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) are natural. Almost 65% of DRC is covered with tropical forests. The main valuable trees in the forests are mohagony, ebony, iroko, obeche and rosewood. Others are palm trees and rubber trees.
a) They provide timber and logs which are exported to earn the country foreign exchange.
b) Timber and logs are used to build and to make valuable furniture.
c) They are major water catchment areas.For example, they are sources of rivers in DRC and other neighbouring countries.
d) They provide raw materials for making medicines, dyes, gum and paper.
e) They are habitats for many wild animals,birds and insects therefore promoting tourism.
f) They are a source of food like fruits, leaves and roots.
g) They are sources of fuel like fi rewood and charcoal.
h) They provide beautiful sceneries.
i) They create job opportunities thereby improving the living standards of people.
j) They have led to the development of other industries. For example; pulp industries.
k) The log from hardwood trees are used in the contruction of bridges.
l) Difference tree species are used to extract medicinal substance which are sold locally and internationally.
1) The forests are very dense making movement and harvesting of trees expensive.
2) Deforestation leads to destruction of rare species therefore, making them extinct.
3) Heavy rainfall and impassable roads make the harvesting and transportation diffi cult.
4) Because of their big sizes and bulkiness, it is diffi cult to cut and transport them.
5) Valuable species are scattered therefore making harvesting diffi cult.
6) Wild animals make the industry dangerous.
7) Outbreak of fi re destroys the forests.
8) Civil wars and unrest in the country makes it difficult to exploit the forest.
9) Exploitation of forest is made difficult by heavy rains that fall almost everyday.
10) Some logs which are transported by rivers may get stuck because they are too heavy to float.
11) Trees have huge trunks that require machines to lift. This makes it difficult for the locals who have simple tools.
12) Presence of water falls inthe rivers makes transportation of the logs along the rivers difficult.
Forests in Swaziland are planted or are exotic. There are large plantations of trees in Swaziland making it the largest country in Africa with plantation forest. Example of trees planted in the plantations are: pine, cypress and eucalyptus.
These plantations are owned by the government and private timber and pulp firms.
a) It is a source of employment to many, therefore, raising the living standards of people.
b) Timber and its products exported to other countries earn the country foreign exchange.
c) It has led to the development of timber related industries.
d) It provides raw materials for pulp industries building, construction and furniture making.
e) It is a major source of fuel. For example,firewood and charcoal.
f) It modifies climate.
g) It reduces soil erosion. They also act as water catchment areas.
h) The forests provide a home for wildlife.
i) The forest add beauty to the environment and some forests are tourist attraction sites.
j) Swaziland sells her timber to othar countries. This has improved her international relations and understanding with other countries.
a) High rate of deforestation than reaforestation affects the forest cover.
b) Outbreak of fi re destroys forests.
c) Ever increasing demand of land for agriculture poses a great threat to the
forests.
d) Diseases and pests attack and destroy them.
e) Severe drought in some parts of the country affects the process of planting. This also causes some trees to dry.
f) Many timber industries pay low wages to those employed in industries. This makes workers to look for alternative jobs.
j) Clearing of forest to create room for settlement.
h) Poverty encourages the use of wood fuel leading to high rate of deforestation.
i) Frequent fire ouybreaks destory forest.
j) Profits from the sales of forest products are not evenly distributed. Kings get large shares tha subjects. This does not improve the lives of the subject much.