They breathe in air and release air from their bodies

They reproduce

They feed

They grow

They remove waste (excrete) (Please note the spelling of "excretion" has no "a")

They move from place to place or parts of their body like plants do.

They sense (react to the changes in environment).
1. Find food.
2. Find partners with whom to reproduce.
3. Identify enemies or predators that may harm them.
4. Escape from these enemies or predators.
5. Identify the presence of harmful things such as poisons like gases, fires and rotten food.
These are:
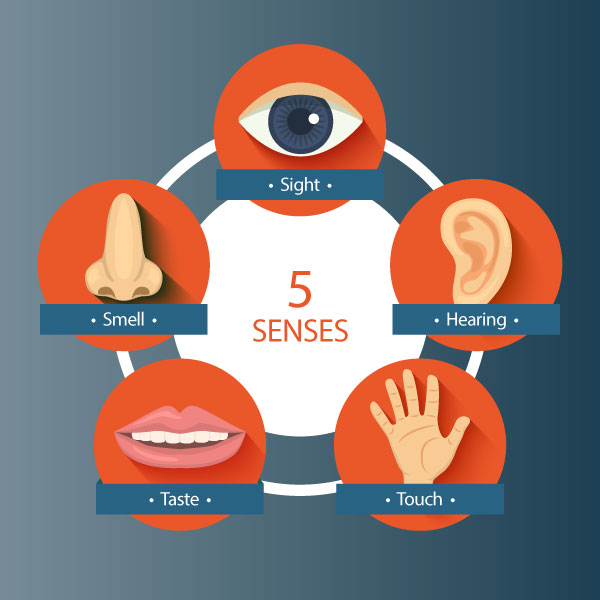
The eye is a sense organ for sight. The human eye is found in the socket or orbit found in front of the head.
The eye is shaped like a ball therefore called ‘eyeball’.
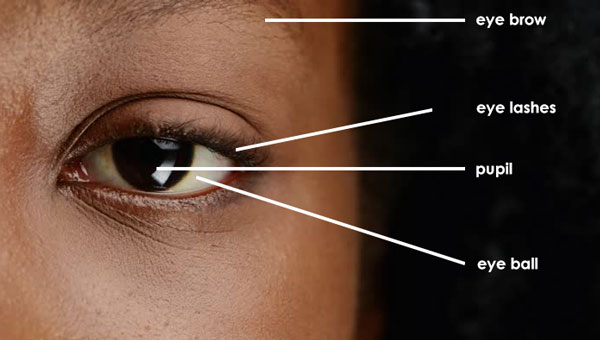
The eyeball is attached to the socket by muscles. The eye is used to see properly care is a must to avoid infection and to prevent any damage to the eye.
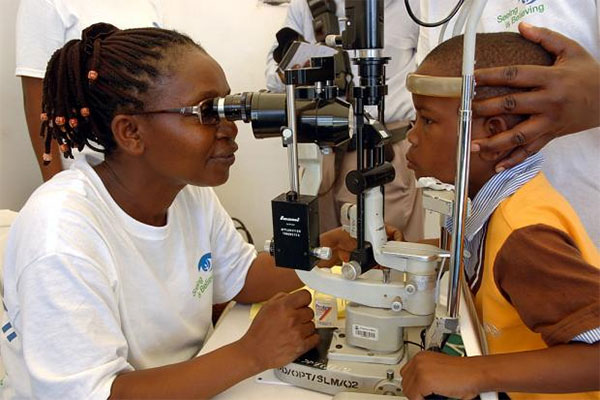
The strength of the eyes is measured by how clearly one can see far or near objects. In a hospital, eye checking involves standing about two and a half metres away from a board with letters written in different sizes.
A person is then required to close one eye and read the letters as they are pointed out by the OPTICIAN.
Thereafter, one is supposed to close the second eye and read with the other eye.
The sense of sight helps us to tell:

The eye is a very important part of the body that must be well taken care of.
The ear is a sense organ for hearing. The outer ear or pinna is at the side of the head.
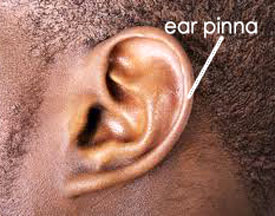
It helps to concentrate and direct sound into the ear. There is a passage leading from the pinna into the inside of the ear. This passage directs sound into the ear.
The passage has a skin called the eardrum that connects the outer ear to the inner ear.
The passage of the ear must be protected from harmful things. This passage produces some substance called wax, which traps dirt to prevent harmful things and particles from entering the ear.
The wax must be cleaned out as often as possible as it may affect hearing if too much of it accumulates in the ear.
A person who cannot hear is said to be deaf and learns to communicate using sign language.
Too much ear wax may lead to deafness but can be cleaned using cotton buds.
A deaf person is an able person with rights like every body else. The ear should therefore be cleaned regularly.

We can use our body parts to communicate with each other without necessarily using words.
This kind of communication is referred to as the use of gestures. Gestures can be classified into facial and body gestures.

This is the sense organ for tasting. The parts of the tongue that sense the taste are called taste buds. There are different taste buds for the different tastes.
These tastes include:
It is important to take care of the tongue. This is done by brushing it using a soft brush to remove remains of food particles.
Cleaning the tongue ensures that the taste buds remain fresh and produce good breath.
The nose is the sense organ that detects smell.
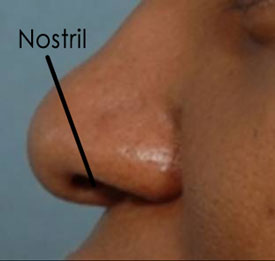
The inside of the nose has a sensitive, moist lining. What the nose smells is usually in gaseous form.
To be able to sense different smells, the sensitive lining of the nose should be exposed to the environment by regular cleaning of the mucus in the nose.
Rough objects should not be used to clean the nose as they may injure the delicate inner lining and this could lead to nose infections.
Colds which cause the secretion of mucus reduce the strength of the sense of smell.
Below is a photography of human skin on a cold morning notice the pimples on it. Why do the pimples form?
The skin is the sense organ for feeling or touch.
The sense of touch helps us to identify and distinguish between varieties of texture whether rough or smooth, hard or soft.
By touching, we can also tell the shape of an object.
Some parts of the body are more sensitive to touch than others.
Fingertips are more sensitive than other parts of the body.
Other sensations the skin can help identify are:
1. Pressure
2. Temperature
3. Pain
These are gestures made by the face to communicate information such as emotions. For example;

These are communication gestures using other parts of the body apart from the face.
Body gestures include nodding the head as a sign of agreement, shaking the head to imply denial or disagreement and shrugging to show a non-caring attitude.
Deaf people communicate through gestures example is the "I love you"sign below.

This is called sign language.
Traffic police communicate with motorists on the road through gestures, which is a special type of sign language.

Nearsightedness also called myopia may develop in a child because of spending too much time reading or looking at a computer.
Study the image below:

To prevent this it is good to ask the optician to issue the child with reading glasses so that the eyes are not damaged during reading.
Play this video:
People who are either short sighted or long sighted can help correct the sight defect by wearing appropriate spectacles that enable them to see better.
