Water that has particles or germs in it is not good for use especially for drinking whether by human beings or other animals.
This kind of water is said to be contaminated. Contaminated water can spread diseases.
Diseases that get to healthy people through contaminated water are called water-borne diseases.
Some water-borne diseases are cholera, typhoid, and bilharzia.
Cholera is a water-borne disease that infects people who handle or drink contaminated water or eat contaminated food.
Water gets contaminated by faeces from an infected person that has not been disposed of properly.
[resource: 1386, align: left]
1. Frequent passing of watery stool (diarrhoea).
2. The victims become dehydrated due to the loss of water in the stool.
3. If unattended to by a medical person, the victims become unconscious, go into a coma and may die.
1. Boil drinking water.
2. Maintain good hygiene by washing the hands with soap and clean water before meals and after visiting the toilet.
3. Cooking utensils should be washed thoroughly with hot water.
4. Foods that are eaten raw like fruits and vegetables should be washed thoroughly with clean water before they are eaten.
5. Maintaining proper sanitation or cleanliness of the surrounding through:
a) Disposing feaces in the right way either in the toilets or latrines not in the bushes.
b) Keeping the toilets and latrines clean.
c) Covering the openings of pit latrines after use to prevent flies from getting to the faeces and then visiting our homes.
d) Burying or burning rubbish in the compound
6. Those infected should:
a) visit the doctor as soon as possible.
b) drink plenty of liquids to regain water that is lost from the body.
c) drink oral rehydration solution or sugar-salt solution. Oral rehydration salt (ORS) is a packet containing some minerals like salt and is available commercially.
One packet of ORS is mixed with one liter of clean water in a clean container and stored in a safe place.
The ORS and water are stirred until the ORS dissolves. After passing stool, the patient should drink a cup of the ORS drink.
If the patient does not have ORS, a salt sugar solution (SSS) can be made.
The salt sugar solution (SSS) can be made by adding, one teaspoonful of salt and eight teaspoonfuls of sugar into a liter of clean water.
This should be stirred until the mixture of water, salt and sugar dissolves. One glass of
SSS should be taken every time after passing watery stool.
Bilharzia is a water-borne disease. The germ that causes bilharzia is carried by snails that live in freshwater ponds.
When the disease-causing germs leave the snail, they easily penetrate into a person’s body through the skin.
They then get into the blood system, then into the bladder or intestines. Fertilized eggs are passed out of the body through urine or faeces.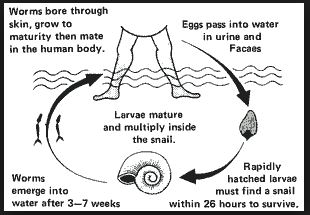
1. Coughing and sneezing.
2. Victims experience abdominal pain especially when passing stool.
3. Passing of urine or stool with blood.
4. Loss of blood which may lead to anemia. Anemia is the shortage of blood in the body.
1. Wearing protective clothing such as gumboots and gloves when handling or walking in stagnant water for instance in the case of rice farmers.
2. Boiling drinking water.
3. People should avoid bathing in stagnant water.
4. Using chemicals called molluscicidal to eliminate snails in water.
5. Proper disposal of human waste to prevent them from getting to water sources.
Standard 6
1. Juma and his children always plant rice seedlings in their flooded shamba. Which of the following diseases is Juma and his children most likely to suffer from?
A. Bilharzia B. Cholera C. Dysentery D. Typhoid