Soil is made up of:
Soil is formed when rocks break down into smaller particles.
These small rock particles contain minerals in them.
The mineral salts found in these mineral particles are essential for plant growth
Did you know we use minerals every day?
Without minerals, you wouldn't be able to clean your teeth or wash your clothes!
Can you think of which mineral do you eat every day?
Different living organisms live in soil.
Some of these organisms are insects, worms, viruses and bacteria.
These living organisms play a very important role in the soil.
Bacteria for example help in making dead plants and animals to decay faster a process called DECOMPOSITION.
These animals also turn the soil making it loose and therefore allowing air to get into the soil.
Some other animals for example termites may harm plants as they feed on the plant roots and stem.
To find out the presence of animals in soil, one needs to collect a sample of soil and observe it.
Use gloves if you are to carry out this exercise.
Humus
Also refered to as the organic matter found in soil also helps in retaining water and minerals, preventing them from being washed away by rain water when it rains.
It also helps in reducing soil erosion.
To find out the presence of organic matter in soil,
i. Collect the soil and put it in a clear plastic jar
ii. Pour water in the jar
iii. After the mixture settles, what is seen floating on top of water is organic matter.
Water exists in soil as a thin layer that surrounds the soil particles.
Some of this water comes from rain though some come from the groundwater.
This water is very important for plants as it is used by the plants in producing food through PHOTOSYNTHESIS.
This is the water that plants rely on when the weather is dry and days pass without the plants being watered.
Soil water helps in dissolving mineral salts that are then taken up by the plants through the plant root.
This water is also used up by the living organisms that are found in soil.
We can preserve this water by MULCHING around the plant to stop it from evaporating.
The spaces that exist between the soil particles are filled with air.
The larger the soil particles, the more air spaces there are in the soil.
This means that sand soil contains more air spaces than clay soil.
The air in the soil is necessary because the animals living in soil need this air.
Plants also need this air to help in absorbing minerals from the soil.
When the animals living in soil move about, they turn the soil thereby creating more air spaces.
When digging, we also turn around the soil and make it loose and creating more air spaces in it.
Organic matter refers to the remains of dead plants and animals that are usually found on top of the soil. It is dark brown in colour.
Organic matter forms HUMUS, which is very rich in nutrients.
Plants use hummus as a source of their nutrients.
Animals in the soil also use hummus as a source of food.
Soil that has humus is usually dark.
Standard 4
1. A lump of soil was placed in a container. Water was then poured into the container. bubbles of air were seen rising in the water as shown in the diagram below.
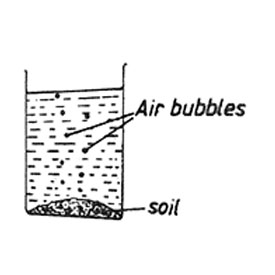
This experiment showed that
A. Soil contains air. B. Water contains air.
C. Air is formed when water is mixed with soil.
D. Air comes from small animals in the soil.
2. Which one of the following does NOT happen when loam soil is strongly heated?
A. Humus content decreases.
B. The volume of air in the soil increases.
C. Amount of water in the soil decrease.
D. Organisms in the soil are killed.
3. Four different types of soil P, Q, R, and S were weighed. They were then heated gently until there was no change in weight.
The results were as shown in the table below.
|
Soil type |
Weight before heating (g) |
Weight after heating (g) |
|
P Q R S |
36 25 44 27 |
31 18 40 25 |
The soil type which had the largest amount of water was
A. P B. Q C. R D. S